What are the Three Main Types of Accounts: A Clear Overview

Retained earnings are profits that have been earned by a company but not distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends. Instead, these profits are kept in the business and used for various purposes, such as reinvesting in the company or paying off debt. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
- Equity accounts accumulate over time, reflecting the long-term financial health and ownership structure of the business.
- These accounts are used to track the company’s financial obligations to its creditors, such as suppliers, lenders, and other entities.
- Inventory accounts represent the stock of goods that a business holds for sale.
- Let’s say you have a cash account balance of $30,000 at the end of 2021.
- Instead, the balance at the end of one period becomes the beginning balance for the next period.
Asset Accounts
It helps investors and creditors assess a company’s ability to generate cash and manage its cash flow. The balance sheet is useful for investors and creditors to assess a company’s liquidity, solvency, and financial stability. Owner’s equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company that belongs to the owners of the business. This includes the original investment made by the owners, as well as any profits that have been retained in the business over time.
Equity
Examples of real accounts include cash, inventory, and property, plant, and equipment. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. Lack of communication between different teams involved in financial management can lead to challenges in managing temporary and permanent accounts. It’s essential to establish clear lines of communication to ensure everyone is aligned. Effective communication helps businesses to avoid accounting errors and enables effective decision-making. Permanent accounts are balance sheet accounts that are not closed at the end of an accounting period.
Order to Cash
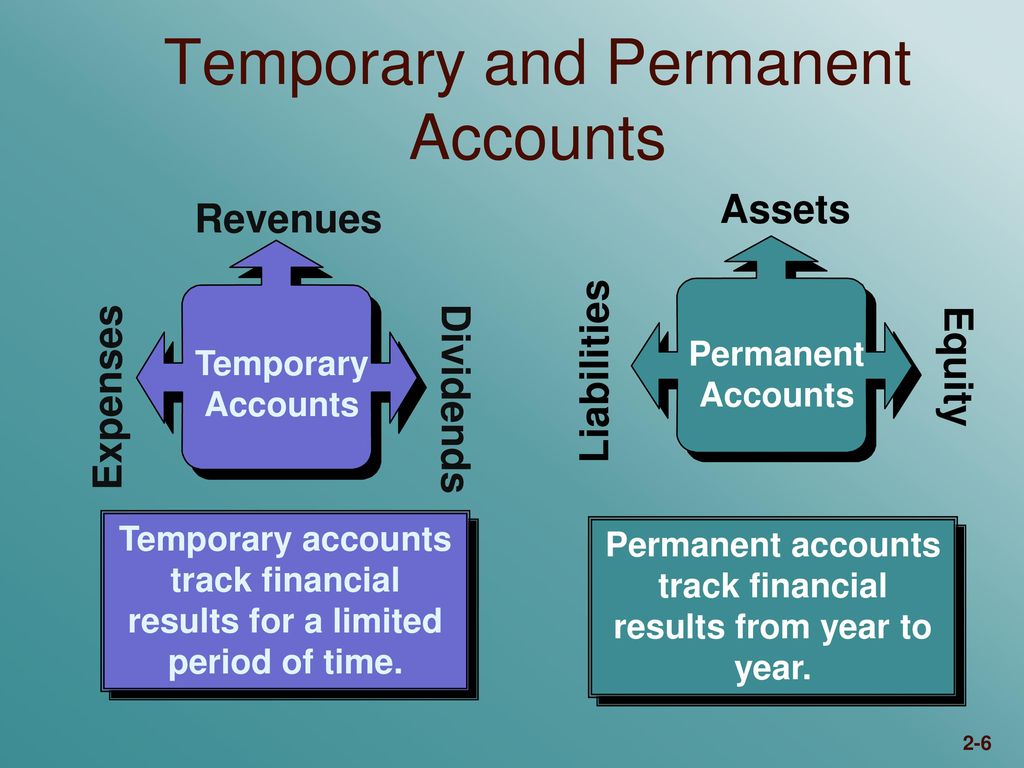
Because you did not close your balance at the end of 2018, your sales at the end of 2019 would appear to be $120,000 instead of $70,000 for 2019. A closed account is any account that has been closed out or otherwise terminated, either by the customer or the custodian. These accounts track the resources owned by a business that provide future economic benefits. Unlike temporary accounts, asset balances carry over from one accounting period to the next and reflect the company’s financial position over time. Permanent accounts, such as assets and liabilities, carry their balances forward, showing the ongoing financial status of the business. These accounts track all costs incurred by the business to maintain operations within an accounting period.
Cash Application
Temporary accounts, such as revenue and expenses, are closed at the end of each period, so they start fresh in the next one. In contrast, permanent accounts, such as assets, liabilities, and equity, carry forward their balances from one period to the next. Efficient management of these accounts helps prevent errors and makes financial reporting easier. Further, automation tools can enhance this process, ensuring sound financial management.
Real account vs. personal account
The balances of these accounts are not reset to zero at the end of each accounting period but instead, carry forward continuously to subsequent accounting periods. In sole proprietorships and partnerships, drawing accounts track withdrawals taken by owners for personal use. In corporations, dividend accounts record which of the following accounts are permanent the profits distributed to shareholders. At the end of the period, the balances in these accounts are closed and transferred to retained earnings or capital. Temporary accounts include revenue, expense, and gain and loss accounts. Permanent accounts are the accounts that are reported in the balance sheet.
Capital refers to the amount of money that a business has invested in itself, while investments refer to the money that a business has invested in other companies or assets. The traditional approach to accounting is a widely used method of bookkeeping that involves recording financial transactions in a chronological order. This approach is based on the principle that every transaction has a dual effect on the financial statements, which is known as the double-entry system. Expense accounts are a type of account used to track the expenses of a business.
The balances in these accounts should increase over the course of a fiscal year; they rarely decrease. The balances in temporary accounts are used to create the income statement. Temporary accounts in accounting refer to accounts you close at the end of each period. Temporary accounts are always closed at the end of an accounting period and start the next accounting period with a zero balance. Permanent accounts always maintain a balance and start the next period out with the ending balance from the prior period.